Contents
- Opportunity for Overseas Financial Companies General Remarks – Political Effort – Support for Overseas Financial Companies
- Regulatory Overview for Overseas Asset Managers Unit Trust/Mutual Fund – Partnership Type Fund (LPS etc.)
- Actual Registration Procedure (1)Financial Instruments Busine – (2)Fund for Small Group Professional Investors –
(3)Specially Permitted Business During the Transition Period/Specially Permitted Businesses for Overseas Investors, etc. –
(4)Financial Instruments Business Operator to sell the fund as an Agent - Other Asset Management Businesses Discretionary Investment Business – Investment Advisory and Agency Business
General Remarks
It is a national policy to revive Tokyo as an International Financial Center.
The Japanese Government is doing its best to attract foreign financial companies, and the registration process for Asset Management Businesses will be completed within a few months at the earliest.
Tokyo is about to revive as International Financial Centers with many incentives, including living supports and visas for Foreign Financial Companies.
We strongly suggest taking advantage of this opportunity.
Political Effort
From 2017, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government has set out a policy to overcome competition with Hong Kong and Singapore in Asia and regain its position as an International Financial Center alongside London and New York in the “International Financial City / Tokyo Concept.”
The Japanese government, the Financial Services Agency, is vigorously promoting Foreign Asset Managers’ entry into Japan as a national growth strategy.
As part of these efforts, the “Create a guidebook to support the application for registration of the financial industry” is indicated in the “Growth Strategy Follow-up” decided by the Cabinet in June 2019. And The Financial Services Agency published the “Guidebook for Registration of Investment Management Business and Other Financial Instruments Businesses” on January 10, 2020, and explains the details of the procedures for registration of Investment Management Business or Investment Advisory and Agency business, that was not disclosed previously.
The Financial Services Agency’s Council “Market System Working Group” published its first report on December 23, 2020, proposing the development of systems for the acceptance of Overseas Asset Managers. Concerning this proposal, the Financial Services Agency has submitted to the Diet a bill to amend the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act to introduce a time-limited system, “Special Permitted Business during Transition Period,” and
“Specially Permitted Businesses for Overseas Investors, etc.” which is a permanent system.
Besides, the Financial Services Agency has begun reforming the regulation and supervision system to create a user-friendly environment to facilitates overseas companies’ business operations. In January 2021, the Financial Services Agency set up a “Local Office opening center” to improve and simplify overseas Asset Managers’ regulatory supervision, such as translating financial administration into English and one-stop service.
Furthermore, it is confirmed that the effective personal tax will be imposed as separate tax (20.42 %) only, not comprehensive taxation (up to 55%) by tax measures related to international financial hub transactions. It will be applied if the fund manager receives income in the form of preferential profit distribution as a GP. It is a low tax rate, not much different from the personal income tax rate in Hong Kong and Singapore. In addition, it will be allowed performance-linked salaries for officers, which was not previously permitted under the personal income tax law, and foreign property of foreigners residing in Japan is exempted from inheritance tax.
Support for Overseas Financial Companies
Our Group positions the support of Overseas Financial Companies, including overseas Asset Managers, as our core business. Attracting foreign financial businesses is a national strategy of the Japanese Government.
In order to pass the wealth to the next generation in Japan (where a declining birthrate with an increasing aging population), it is necessary to establish Tokyo as a financial center. We find our business is rewarding.
Our Group provides a wide range of one-stop services for international financial institutions for registration/license application and other procedures and business support to expand business in Japan by our staffs who have the experience to work in the financial industry, including our representative.
In addition to providing legal and administrative procedural support, we have supported Japanese market entry for foreign financial institutions and businesses and set Japanese bases for overseas funds. Furthermore, we have carried out hands-on support.
Furthermore, we have track records to support foreign financial institutions entering into the Japanese Market in cooperating with consulting firms, foreign law firms, Japanese companies, and individuals in charge of the domestic contact point.
Please feel free to contact us if you wish to collaborate with us to support foreign financial institutions entering the Japanese Market.
Regulatory Overview for Overseas Asset Managers
The details of the regulatory application to Overseas Asset Managers differ depending on the type of business and the legal scheme of the assets. Some types of business can be entered relatively quickly and at a low cost depending on the scheme. And some types have challenging to enter. It is not easy to describe the entire regulatory system.
In general, it is difficult for us to make a practical analysis to enter into the Japanese Financial Market with information such as “I want to sell an American fund in Japan.” It is necessary to analyze the based on precise information regarding Fund Investment Scheme, Financial Instrument (Target Business to invest), Business License, and Target Investors.
If you are exploring Overseas Asset Managers to enter the Japanese market, please get in touch with us. We will understand the detail and propose the best solution.
Unit Trust/Mutual Fund
Offering
The solicitation of investment trust-type funds to residents falls under the Financial Instruments Business.
A self-offering or private placement of the investment trust beneficiary certificate falls under the Type II Financial Instruments Business. An offering or manage private placements of the investment trust beneficiary securities falls under the Type I Financial Instruments Business.
However, the registration obligation may be exempted due to the special provisions of foreign securities companies if the resident purchases the securities voluntarily without active solicitation.
Investment Management
There are no restrictions on “Investment Management” at the foreign country as a trustee of a foreign investment trust held by a resident. This regulation regarding foreign investment trust entrustment business sets up an investment trust by themselves and manages it as a trustor.
It is required to register the Investment Management Business in Japan If you manage a foreign investment trust issued at the Cayman Islands on a discretionary investment contract. Still, the investment management is carried out from Japan.
It might be a little confusing; it is required to register the Financial Instruments Business if you actively carry out investment trust sales in Japan and investment management from Japan.
Investment Management Business for Professional Investors
There are some relaxations in registration requirements for the investment trust business only for professional investors.
When investing an investment trust from Japan under a discretionary investment contract and selling the investment trust beneficiary securities in Japan, the solicitation or private placement of the funds falls under the Type I Financial Instruments Business in principle even if the investment trust is managed under the discretionary contract.
However, if it falls under the Investment Management Business for qualified investors (mainly for institutional investors), it will be classified as a “Deemed Type II Financial Instruments Business” rather than the Type I Financial Instruments Business. Therefore, it is possible to manage investment trust beneficiary securities based on discretionary investment contracts by registering the Type II Financial Instruments Business.
Partnership Type Fund (LPS etc.)
Offering
The solicitation of Partnership-Type funds to residents falls under the Type II Financial Instruments Business. Unlike “Specially Permitted Businesses for Overseas Investors, etc.” there is no explicit exemption from registration obligation for solicitation of collective investment scheme type fund.
Therefore, there is to conclude a collective investment scheme contract with a resident will fall under as an unauthorized business.
It means that it is illegal to solicit the collective investment scheme type fund for residents (regardless of whether they are professional or non-professional Investors) if you are not registered and have not been notified for “Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.”
Then, what happens if an investor voluntarily applies for a fund and there is no solicitation relationship. It is a gray zone, and there is no clear precedent.
Investment Management
Regarding the regulation of Investment Management, it falls under the Investment Management Business if the fund mainly (more than 50% of assets) invest in securities or derivative transactions owned by the resident. However, certain foreign funds run by foreign fund managers are exempt from the registration obligation.
Registration is not required for “Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.” or small-group funds that direct and indirect beneficiaries are only qualified institutional investors and the majority of investors are not Japanese residents.
Article 16, Paragraph 1, Item 13 of the Cabinet Office Ordinance on Definitions under Article 2 of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act.
Among the foreign partnership-type funds, it is not required to register the Investment Management Business (Fund Management Business) for the management business of overseas funds that meet the following conditions.
⒜ Only domestic investors (direct investors) who directly invest in the fund are qualified institutional investors or those who have filed “Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.”
⒝ Only domestic qualified institutional investors (indirect investors) invest with the fund of funds scheme.
⒞ The total number of direct and indirect investors is less than 10.
⒟ When the funds contributed by the direct investor are less than 1/3 of the total investment amount of the fund
Requirement of Registration or Notification
However, there is no explicit registration exemption provision for offering or private placement, even though the Financial Instruments Business registration is exempted due to the provisions mentioned above. Therefore, a Financial Instruments Business license is required for an offering, even if exempted from registration as domestic investors are only a small number of qualified institutional investors.
In other words, the Type II Financial Instruments Business registration is required for soliciting partnership-type funds (partnership agreements such as LPS and other collective investment scheme interests).
However, it is not required to register the Type II Financial Instruments Business if you entrust investment solicitation (offering or private placement (Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, Article 2, Paragraph 8, Item 9)) to a Type II Financial Instruments Business Operator and do not carry out offering by yourself.
However, it will be classified as the Type I Financial Instruments Business rather than the Type II Financial Instruments Business if the fund interest falls under the security token.
You can carry out private placement and manage the fund with a notification if you use a small-group professional fund (Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.).
Let’s take a closer look below.
Actual Registration Procedure
(1) Financial Instruments Business
There are quite high regulatory requirements for the Type I /Type II Financial Instruments Business and the Investment Management Business. Therefore, it is not easy to register these businesses to carry out the Financial Instrument Business for general investors.
However, it is possible to register if there is a proper business organization and professional human resources. If you want to carry out the Financial Instruments Business for mainly specific investors, it is possible to register within 6 months. Even if the business is for general investors, there are a number of cases where complete the registration within a relatively short time for those with sufficient credibility and sufficient officers and employees.
However, it becomes a higher registration and organization requirement for the businesses that collect funds from small lots and many investors, such as crowdfunding.
There is a difference in registration hurdles between the small number of investors/OTP businesses and many investors/online businesses. If you want to carry out FINTECH business for general investors, you need to prepare for a lengthy procedure for a year or two.
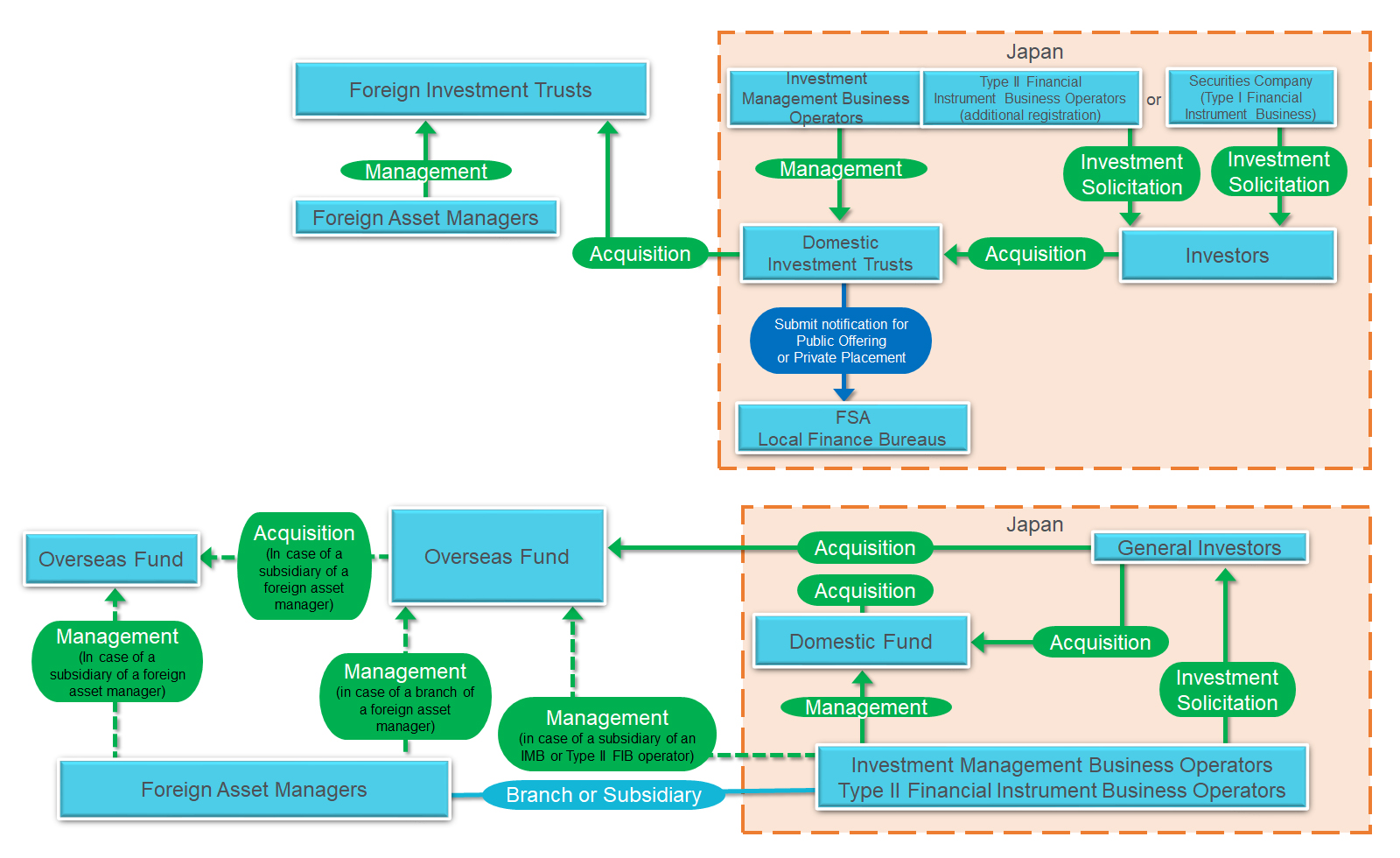
Examples of registration schemes (upper / investment trust-type, lower / collective investment scheme type).
The charts below are all examples of the schemes.
(2) Fund for Small Group Professional Investors
It is legal if the fund management company carries out self-offering and investment management while submitting a notification of “Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.” in advance and there are 1 or more domestic investors and 49 or less qualified institutional investors. (Article 63 of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act).
It is a small-group professional fund and one kind of professional fund that can start relatively quickly and at a low cost. This is the most accessible business scheme for the domestic offering of foreign funds for Professional Investors.
It is a highly well-organized scheme as a professional fund, such as entering without establishing an office in Japan and completing the notification procedures in English. It is similar to deregulated concept for Accredited Investors and Sophisticated Investors in Europe, the United States and Singapore.
In addition, even overseas financial institutions and corporations can transition to “Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.” by submitting a notification if they meet the requirements. Therefore, a collective investment scheme type Fund (LPS etc.) for foreign institutional investors can easily meet the requirements of this notification.
Even registering the Type II Financial Instruments Business, it is not easy to carry out offering or privately place overseas GP funds for “retail.” Therefore, if you want to offer overseas funds, the 1st option is to offer to institutional investors under the scheme of “Specially Permitted Businesses for Qualified Institutional Investors, etc.”
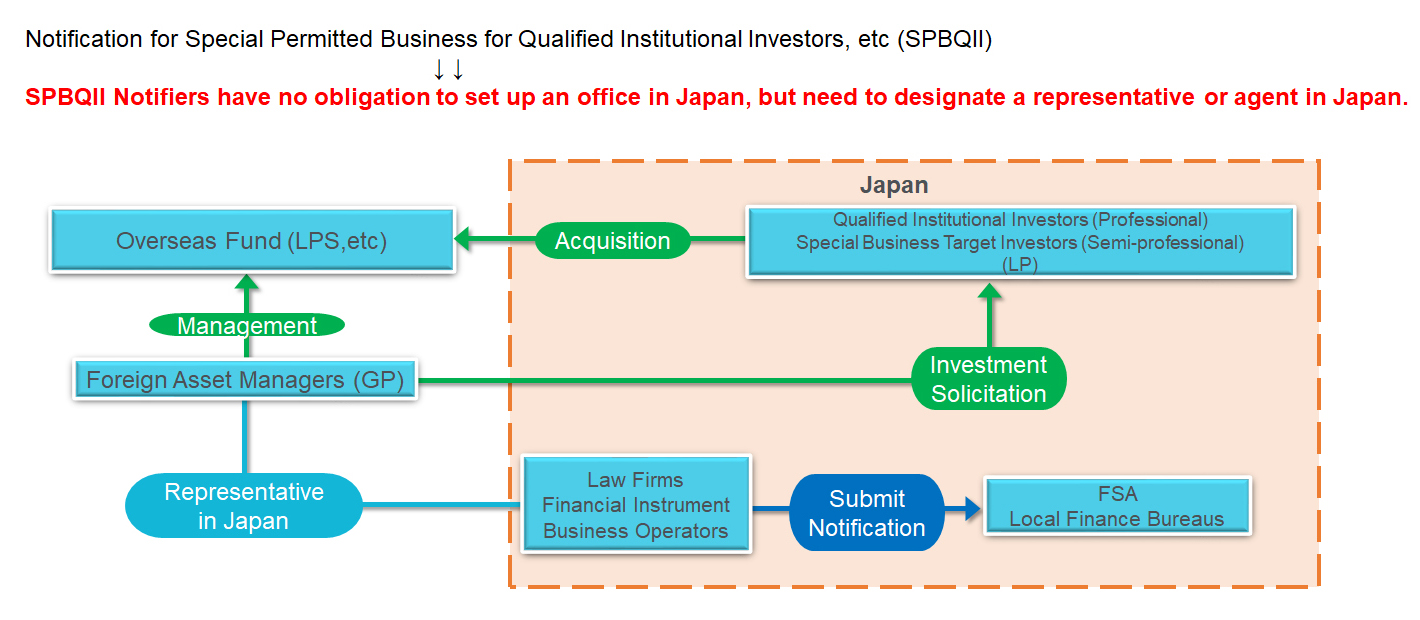
(3) Specially Permitted Business During the Transition Period/Specially Permitted Businesses for Overseas Investors
In the amendment bill of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act in 2021, new business schemes will be introduced, such as “Specially Permitted Business During the Transition Period” and “Specially Permitted Businesses for Overseas Investors, etc.”
The “Specially Permitted Business During the Transition Period” allows foreign Investment Managers (who manage the Fund with overseas funds) to carry out their business in Japan.
The “Specially Permitted Businesses for Overseas Investors, etc.” allows to carry out Collective Investment Scheme funds with overseas funds (more than 50%) while domestic investors are limited to qualified institutional investors. It will be required a simple notification but necessary to establish an office in Japan.
The COVID-19 Pandemic has dramatically reduced international traffic. However, Financial Centers in Asia are shifting to Singapore. The Japanese Government is being questioned about its seriousness of whether the new scheme will enhance the concentration of financial businesses in Tokyo.
(4) Financial Instruments Business Operator to sell the fund as an Agent
It is common that (Foreign) Investment trusts are offered or privately placed by securities companies (the Type I Financial Instruments Business operators). Similar to the foreign investment trust sales schemes, the Type II Financial Instruments Business Operator sells collective investment schemes mainly for major institutional investors on behalf of the fund.
However, it is not possible to solve the Asset Management registration issue by selling the fund through the Type II Financial Instruments Business Operator for mainly in securities or derivative transactions (more than 50% of assets) except for a small number of professional funds (the exemption as mentioned above from registration or notification of funds).
Therefore, the Type II Financial Instruments Business Operator can sell the funds that do not fall under securities (more than 50% of assets) or derivative transactions, or funds for institutional investors only which exempted registration.
The Type II Financial Instruments Business registration requirement is more manageable than those for the Investment Management Business. It is relatively easy for alternative funds (that appropriately disclose and explain investment details to regulatory agencies) to enter Japan. On the other hand, real Estate Funds can’t be sold by the Type II Financial Instruments Business license only.
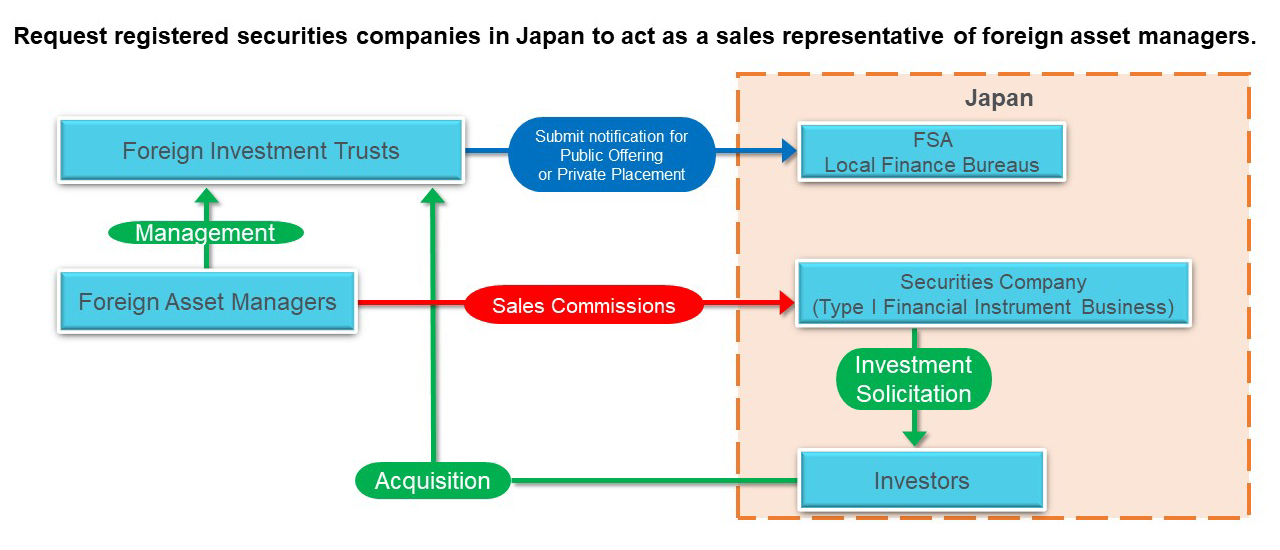
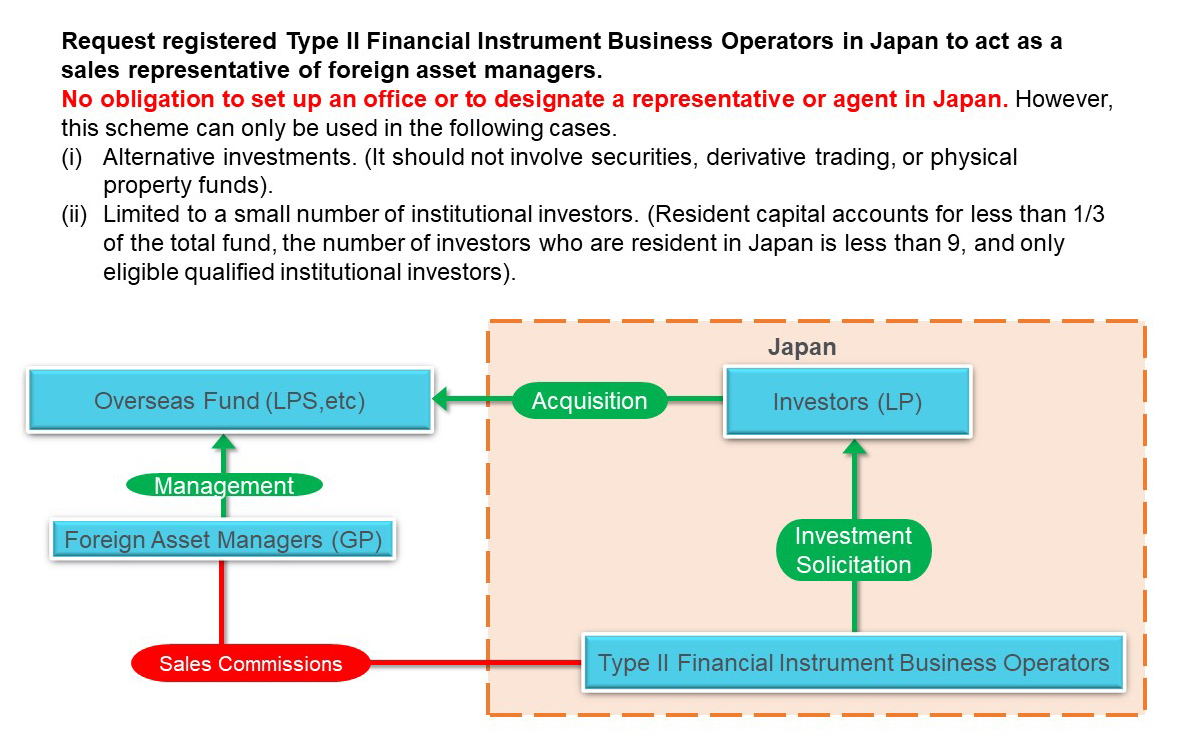
Other Asset Management Businesses
Discretionary Investment Business
EAM business, Corporate Investment Fund, Wrap Account, and other business that manages a customer’s assets under the name of an investment adviser are called Discretionary Investment Business, which is classified as “Investment Management Business” under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act.
Discretionary Investment Business is sometimes used for fund management,
by concluding a Discretionary Investment Contract with a company that manages the fund as a GP, or
by concluding a Discretionary Investment Contract with a company that manages an investment trust as a trustee.
Many companies manage funds with Discretionary Investment Contracts.
Discretionary Investment Contracts do not keep the client’s assets. Therefore, it is easier to register than the fund business and investment-related business in terms of the required staff and the operation management.
Especially in the business for wealthy people, there is a need to provide only operational instructions and advisory under the name of the customer or family office, instead of entrusting funds from the customer.
The Discretionary Investment Business and the Investment Advisory and Agency Business(described below) suit those family office asset management.
The investment Management Business includes Investment Company Asset Management Businesses such as REITs.
Investment Advisory and Agency Business
The Investment Advisory and Agency Business provides investment advice from the customer’s point of view.
It is not easy for overseas financial companies to take over Japanese financial institutions and investment advisors and develop FA and PB business for wealthy people and companies in Japan.
However, many Overseas Asset Managers want to register the Investment Advisory and Agency Businesses. Our Group has track records of supporting Overseas Asset Managers to register advisory and agency.
It means that there are still many wealthy people in Japan, and that Japanese stocks, real estate, and other assets are still attracting international attention as investment targets. There is a considerable need to open an office in Japan to collect information and provide investment advice to SPCs and other vehicles in their home country.
Our Group proposes the fastest and cost-efficient strategy for the Investment Advisory and Agency Business registration.
Special feature: Promotion of entry of overseas asset managers
The Financial Services Agency is encouraging the entry of overseas asset managers, and else, with the aim of establishing Japan’s position as an international financial center open to the world.
Full-scale regulatory reforms are underway, such as tax reform, the establishment of The special business for overseas investors and The special business for the transition period, and simplification of procedures.





